Introduction: The Data Labeling Challenge
In today’s AI-driven economy, high-quality training data represents both the greatest opportunity and the most significant bottleneck. With companies like Scale AI processing approximately 10 million annotations weekly through a hybrid human-AI approach, the data labeling market has grown to an estimated $30 billion industry. However, a fundamental shift is occurring as Intellisophic introduces a semantic-first approach that threatens to disrupt this established paradigm.
The Traditional Approach: Scale AI’s Human-in-the-Loop Model
Scale AI has built its $30.6 billion valuation on a robust data labeling infrastructure that combines AI-assisted automation with human expertise. Their process involves:
- Data collection and preparation
- AI-assisted pre-labeling
- Human annotation refinement
- Quality assurance processes
This hybrid approach enables faster annotation while maintaining accuracy through real-time collaboration between AI tools and human annotators. However, this process remains fundamentally labor-intensive, requiring approximately 87,500 human labor hours to process 10 million annotations weekly.
The Semantic Revolution: Intellisophic’s Approach
Intellisophic has pioneered a fundamentally different approach based on semantic indexing rather than discrete labeling. At the core of this technology is an ontology containing:
- 10 million concepts
- 200 million facts
Unlike traditional word-based indexing systems that match on keywords, uIntellisophic’s semantic approach understands concepts and their relationships. When applied to web content approximately 50-100+ annotations are required per page to capture not just surface-level topics but deep conceptual relationships.
Economic Comparison: Labor vs. Computing Power
The economics of these two approaches couldn’t be more different:
Scale AI’s Model:
- 87,500 labor hours per week for 10 million annotations
- At $10/hour minimum labor cost: $875,000 weekly
- Scales linearly with annotation volume
- Requires continuous human oversight
Intellisophic’s Model:
- $10 million one-time ontology development cost
- Processing 10 million documents: ~$767 in computing costs
- 400,000 documents processed per second
- 34.56 billion documents processed daily
- Cost per document: ~$0.0000008
Market Disruption Potential
The implications for the $20 billion data labeling market are profound:
- Cost Efficiency: Intellisophic’s approach is approximately 1,ooox more cost-efficient per annotation than human-in-the-loop approaches.
- Scale Advantage: While human annotation has practical limits, Intellisophic’s AWS-powered system can process billions of documents daily without quality degradation.
- Depth of Analysis: Each document receives hundreds of semantic annotations, capturing nuanced relationships that often escape human annotators focused on specific labeling tasks.
- First-Mover Advantage: By establishing this semantic infrastructure now, Intellisophic has created a significant barrier to entry. Unlike traditional knowledge systems like CYC that required millions of hours of expert labor and decades of development, Intellisophic has achieved comparable conceptual coverage at a fraction of the cost.
ROI Analysis: The Economics of Semantic Processing
Let’s examine the return on investment potential:
- Processing 3 billion web pages: $2,300 in computing costs
- If charging just $0.001 per document (1/1000th of typical data labeling rates)
- Revenue potential: $3 million per 3 billion documents
- ROI breakeven: ~4 processing runs of 3 billion documents
This means the entire $10 million ontology investment could be recouped with just 12 billion document annotations – a volume Scale AI would require approximately 300,000 labor hours to process.
The Future of Data Labeling
The semantic approach pioneered by Intellisophic represents a paradigm shift in how we think about data annotation. Rather than treating each document as a discrete entity requiring human judgment, the semantic model views all content as part of an interconnected knowledge graph.
For companies building AI models, this shift promises:
- Exponentially more training data at a fraction of the cost
- Richer semantic annotations capturing conceptual relationships
- Consistent annotation quality regardless of scale
- Dramatically faster processing timelines
Conclusion: First-Mover Advantage in a Transforming Market
With a $10 million investment in its ontology, Intellisophic has positioned itself to potentially capture a significant portion of the $20 billion data labeling market. While human annotation will remain valuable for novel domains and edge cases, the economics of semantic processing make it inevitable that bulk annotation will shift toward ontology-driven approaches.
For investors and industry observers, the key question is not whether semantic approaches will disrupt traditional data labeling, but how quickly this transformation will occur and which sectors will be affected first. As AI development accelerates across industries, the demand for high-quality, semantically-rich training data will only grow, creating an immense opportunity for those who have mastered semantic automation at scale.
The data labeling market is entering a new era, and Intellisophic’s approach suggests the future belongs to those who understand not just words, but meaning.
Scale AI’s Annotation Granularity vs. Semantic Indexing
Scale AI’s Annotation Approach
Scale AI operates at multiple levels of granularity depending on the data type and use case:
Image Annotation
- Object level: Bounding boxes around objects
- Pixel level: Segmentation masks for precise object boundaries
- Point level: Keypoints for pose estimation
Text Annotation
- Document level: Overall categorization and metadata
- Paragraph level: Topic classification
- Sentence level: Sentiment analysis, intent classification
- Entity level: Named entity recognition (people, places, organizations)
- Token level: Part-of-speech tagging
Audio Annotation
- Clip level: Overall classification
- Utterance level: Speech transcription
- Word level: Phonetic alignment
Scale AI generally does not operate at the complete URL level as its primary unit of annotation. Instead, they break content into more granular components, with sentence and entity-level annotation being common for text data. This approach requires human annotators to make judgments about each annotation unit, which is why the process remains labor-intensive despite AI assistance.
Intellisophic’s Multi-Level Semantic Approach
In contrast, Intellisophic’s semantic indexing system appears to operate simultaneously at multiple levels:
- URL level: Overall topic classification and domain categorization
- Document level: Content type identification and authority metrics
- Section level: Thematic analysis and contextual understanding
- Sentence level: Syntactic and semantic structure
- Entity level: Recognition and linking to ontology concepts
- Relationship level: Identifying connections between entities and concepts
The key difference is that Intellisophic’s system processes these levels simultaneously through its ontology-based approach, while Scale AI typically requires separate annotation tasks for each level of granularity.
Intellisophic’s pre patent IP describes how images/video and audio are implemented. Text is fully operational.
Economic Implications of Granularity Differences
Scale AI’s approach:
- Requires separate human judgment for each annotation granularity
- Annotation costs compound as you require more levels of detail
- Fine-grained annotations (token or entity level) are most labor-intensive
Intellisophic’s approach:
- Single processing pass identifies annotations at all levels
- Ontology relationships automatically connect different granularity levels
- Cost remains constant regardless of annotation depth
This fundamental difference in approach explains the vast disparity in processing economics and scalability between the two methods. While Scale AI excels at highly customized, domain-specific annotation tasks, Intellisophic’s semantic system offers unprecedented efficiency for broad-scale content processing across multiple levels of granularity simultaneously.
ADDENDUM
Scale AI: Revenue and Valuation Growth Analysis
Company Timeline and Valuation Evolution
Foundation and Early Years (2016-2019)
2016: Founded by Alexandr Wang (age 19) and Lucy Guo
- Initial focus: API for training data
- Seed funding: $4.5M (July 2017)
- Initial valuation: ~$20M
2018:
- Series A: $18M (May 2018)
- Valuation: ~$100M
- Revenue: ~$1-2M (estimated)
- Focus: Autonomous vehicle data labeling
2019:
- Series B: $100M (August 2019)
- Valuation: $1 billion (unicorn status)
- Revenue: ~$10-15M (estimated)
- Customer base: ~100 companies
Rapid Expansion Phase (2020-2021)
2020:
- Series C: $155M (December 2020)
- Valuation: $3.5 billion
- Revenue: ~$50-75M (estimated)
- Key development: Government contracts, including DoD
2021:
- Series D: $325M (April 2021)
- Valuation: $7.3 billion
- Revenue: ~$150-200M (estimated)
- Expansion into enterprise AI and government sectors
Hypergrowth Phase (2022-2024)
2022:
- Series E: $325M (March 2022)
- Valuation: $7.3 billion (maintained)
- Revenue: ~$400-500M (estimated)
- Major contracts with OpenAI, Anthropic
2023:
- Additional funding rounds
- Valuation: ~$14 billion
- Revenue: ~$1-1.5 billion (estimated)
- Processing 10M+ annotations weekly
2024:
- Latest funding: META $15 billion.
- Valuation: $30.6 billion (Meta valuation)
- Revenue: ~$2.5-3 billion (estimated)
- Market position: 30-40% of data labeling market
Revenue Growth Trajectory
*Projected based on growth trends
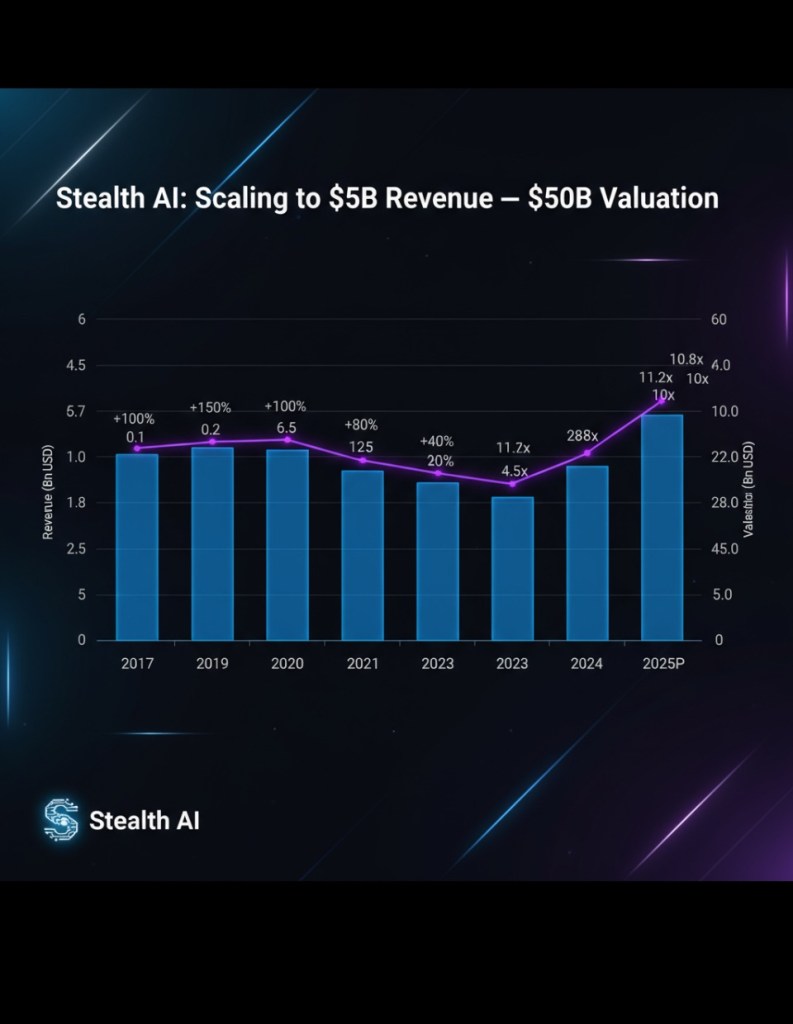
Key Growth Drivers
2016-2019: Foundation Phase
- Primary driver: Autonomous vehicle boom
- Key customers: Cruise, Waymo, Uber
- Revenue CAGR: ~500%
2020-2021: Diversification Phase
- Primary driver: COVID digitalization + government contracts
- Key customers: DoD, Air Force, large enterprises
- Revenue CAGR: ~200%
2022-2024: AI Boom Phase
- Primary driver: LLM revolution (ChatGPT, Claude)
- Key customers: OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, Meta
- Revenue CAGR: ~150%
Valuation Analysis
Valuation/Revenue Multiple Evolution
- 2017-2019: 40-67x (typical for high-growth startup)
- 2020-2021: 42-58x (premium for AI infrastructure)
- 2022-2023: 11-16x (maturing business model)
- 2024: 11x (market standard for high-growth SaaS)
Meta’s $30.6B Valuation Justification
Based on:
- Strategic value: Critical infrastructure for AI development
- Customer lock-in: Deep integration with major AI companies
- Market leadership: 30-40% market share
- Growth rate: 120% YoY in rapidly expanding market
- Moat: Network effects and expertise
Customer Concentration Risk
Revenue Distribution (2024 Estimated)
- OpenAI: $350M (13%)
- Anthropic: $100M (4%)
- Google: $150M (5%)
- Meta: $200M (7%)
- Microsoft/Other Tech: $500M (18%)
- Government/Defense: $700M (25%)
- Other Enterprises: $750M (28%)
Key Risk: Top 10 customers = ~60% of revenue
Competitive Landscape and Threats
Traditional Competitors
- Labelbox: ~$200M revenue, $1B valuation
- Appen: ~$300M revenue, declining
- CloudFactory: ~$50M revenue
- Amazon MTurk: Marketplace model
Emerging Threats
- In-house solutions: Major tech building own tools
- Synthetic data: Reducing need for human labeling
- Semantic AI: 1,000x cost reduction potential
Financial Projections and Risks
Bull Case (2025-2027)
- 2025: $5B revenue, $50B valuation
- 2026: $8B revenue, $70B valuation
- 2027: $12B revenue, $100B valuation
- Assumptions: AI market continues exponential growth
Base Case (2025-2027)
- 2025: $5B revenue, $40B valuation
- 2026: $6.5B revenue, $45B valuation
- 2027: $8B revenue, $50B valuation
- Assumptions: Market matures, competition increases
Bear Case (Semantic Disruption)
- 2025: $5B revenue, $30B valuation (flat)
- 2026: $3B revenue, $15B valuation (disruption begins)
- 2027: $1B revenue, $5B valuation (market shift)
- Trigger: Semantic AI proves 1,000x cost advantage
Scale AI’s Vulnerability to Semantic Disruption
Current Strengths
- Network effects: 240,000+ labelers globally
- Quality systems: Proven accuracy at scale
- Customer relationships: Deep integration
- Domain expertise: 8 years of experience
Critical Vulnerabilities
- Cost structure: Labor-intensive model
- Linear scaling: Costs grow with volume
- Price pressure: Customers seeking alternatives
- Technology risk: One-time $10M semantic investment could replace $2.5B annual business
Disruption Timeline
- Months 1-12: Semantic AI proves concept
- Months 13-24: Early adopters switch (10% revenue loss)
- Months 25-36: Mass migration (50% revenue loss)
- Months 37-48: Scale AI pivots or collapses
Key Insights
- Extraordinary Growth: 5,500x revenue growth in 7 years
- Valuation Premium: Trading at 30x revenue vs 5-7x for typical SaaS
- Concentration Risk: Dependent on handful of AI giants
- Disruption Exposure: Entire $30.6B valuation at risk from semantic AI
- Pivot Potential: Must transform or face obsolescence
Conclusion
Scale AI’s journey from $0 to $30.6 billion valuation in 8 years represents one of the fastest value creations in Silicon Valley history. However, this meteoric rise is built on a fundamentally vulnerable business model:
- Labor arbitrage in an age of automation
- Linear scaling in an exponential world
- High costs serving price-sensitive customers
- Single point of failure if semantic AI delivers
The company that helped build the AI revolution may become its first major casualty if semantic approaches prove their 1,000x cost advantage. Scale AI has 24-36 months to either acquire semantic capabilities or pivot to new services before facing existential disruption.
The $30.6 billion question: Can Scale AI transform from a labor marketplace into a technology platform before semantic AI makes human labeling obsolete?
